ROS 2 Turtlesim Edge Detection
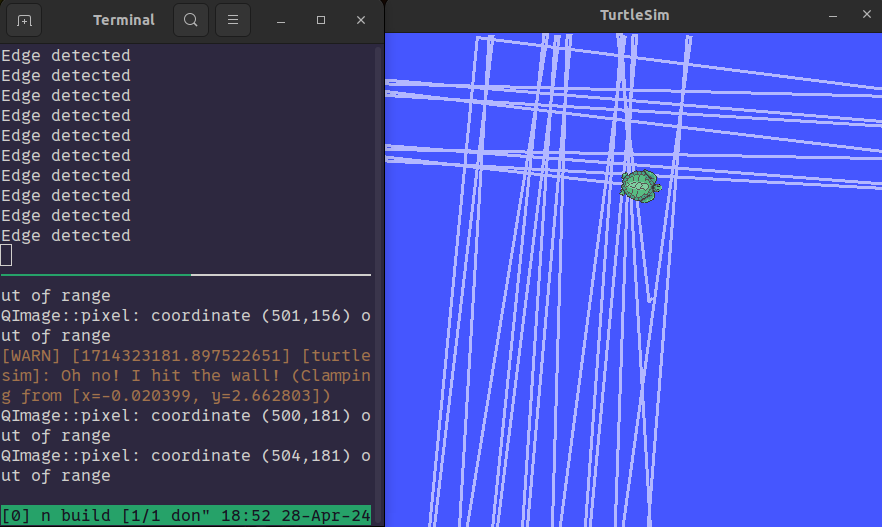
This custom C++ node for ROS 2 will spawn a simulated turtlebot in the center of the screen with a random orientation. It will then drive forward until an edge is detected where it will turn 90 degrees, print “Edge Detected” to the terminal and continue driving. A custom Bash script can install the package.
You can read more about the technical aspects on my Dev Blog
The source code can be found on my GitHub
Tutorial
Once you have Linux set up and running and have successfully ran and controlled the turtle sim node you can start writing custom nodes. Here you can find a brief walkthrough on creating and building an edge detection ROS node for TurtleSim
Creating a package
First we will create our package and node. While in ros2_ws/src we can enter the following into the terminal:
ros2 pkg create --build-type ament_cmake --license Apache-2.0 --node-name edge_detect turtlesimAutomata
When you run this command, it creates a new ROS 2 package named “turtlesimAutomata” with the specified build system, license, and main node name. We now should have a folder in the ros2_ws/src directory called turtlesimAutomata
Your package folder should look like this:

We should have a file in our turtlesimAutomata/src folder called edge_detect.
Modifying node
This is the node we can write code in. We now need to update both the edge_detect.cpp file and the CMake.txt file. First we will write the following into our edge_detect.cpp file:
// include all of our necessary libraries
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "geometry_msgs/msg/twist.hpp"
#include "turtlesim/msg/pose.hpp"
#include "turtlesim/srv/teleport_absolute.hpp"
#include <random>
// define namespace
using namespace std::chrono_literals;
// this function starts the turtle at a random angle in the center of the screen. It uses the teleport_absolute service
void teleportTurtle(const rclcpp::Node::SharedPtr& node) {
//define our service node
auto turtleTeleport = node->create_client<turtlesim::srv::TeleportAbsolute>("turtle1/teleport_absolute");
// state our x and y teleport target
auto request = std::make_shared<turtlesim::srv::TeleportAbsolute::Request>();
request->x = 5.5;
request->y = 5.5;
// Generate a random initial angle between 0 and 360 degrees
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 gen(rd());
std::uniform_real_distribution<float> dis(0, 2 * M_PI); // Define the range for angle in radians
request->theta = dis(gen); // Set the random angle
// run the service and output whether it was successful or not
while (!turtleTeleport->wait_for_service(1s)) {
if (!rclcpp::ok()) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(node->get_logger(), "Interrupted while waiting for service to appear.");
return;
}
RCLCPP_INFO(node->get_logger(), "service not available, waiting again...");
}
auto result = turtleTeleport->async_send_request(request);
if (rclcpp::spin_until_future_complete(node, result) != rclcpp::FutureReturnCode::SUCCESS) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(node->get_logger(), "Failed to teleport turtle");
} else {
RCLCPP_INFO(node->get_logger(), "Turtle teleportation completed");
}
}
// this is our edge detection function, it relies on the x and y postiton of the turtle to determine if it is inbounds or not
void pose_callback(const turtlesim::msg::Pose::SharedPtr msg, const rclcpp::Node::SharedPtr node,
rclcpp::Publisher<geometry_msgs::msg::Twist>::SharedPtr publisher) {
static bool is_rotating = false; // Flag to indicate if the turtle is rotating
static float initial_angle = 0.0; // Static variable to store the initial angle
// Check if the turtle is near the edge
if (msg->x <= 0 || msg->x >= 11 || msg->y <= 0 || msg->y >= 11) {
// If the turtle is not already rotating, initiate rotation
if (!is_rotating) {
geometry_msgs::msg::Twist twist;
twist.linear.x = 0; // Stop
twist.angular.z = -5.0; // Rotate
publisher->publish(twist);
printf("Edge detected\n");
initial_angle = msg->theta; // Store the initial angle
is_rotating = true; // Set the flag to indicate rotation
}
// Check if the turtle has rotated 90 degrees from the initial angle
if (std::abs(msg->theta - initial_angle) >= 1.570796) { // 90 degrees in radians
// If rotation is completed, initiate forward movement
geometry_msgs::msg::Twist twist;
twist.linear.x = 5; // Drive forward
twist.angular.z = 0.0; // No rotation
publisher->publish(twist); // Publish the move instruction to stop rotating
is_rotating = false; // Reset the flag
}
} else {
// If the turtle is not near the edge, initiate forward movement
geometry_msgs::msg::Twist twist;
twist.linear.x = 5; // Drive forward
twist.angular.z = 0.0; // No rotation
publisher->publish(twist);
is_rotating = false; // Reset the flag
}
}
bool initial_state = true; // boolian flag to determine if we are in our inital state
// main loop that will run our code
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
// start node
auto node = rclcpp::Node::make_shared("edge_detector");
// check to see if code has run already, if not we define starting postion for turtle
if (initial_state == true){
printf("Starting\n");
teleportTurtle(node); // start turtle with random thetea
initial_state = false; // reset boolian flag
}
// publish twist
auto publisher = node->create_publisher<geometry_msgs::msg::Twist>("/turtle1/cmd_vel", 10);
// subscribe to turtle pose
auto subscription = node->create_subscription<turtlesim::msg::Pose>(
"/turtle1/pose", 10,
[node, publisher](const turtlesim::msg::Pose::SharedPtr msg) {
pose_callback(msg, node, publisher);
});
rclcpp::spin(node);
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}
However this code will not work until we modify our CMake.txt file with the following:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5)
project(turtlesimAutomata)
# Default to C++17
if(NOT CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
endif()
# Find dependencies
find_package(ament_cmake REQUIRED)
find_package(rclcpp REQUIRED)
find_package(geometry_msgs REQUIRED)
find_package(turtlesim REQUIRED)
find_package(std_srvs REQUIRED) # Add this line to find the std_srvs package
# Add executable
add_executable(edge_detect src/edge_detect.cpp)
# Link against ROS 2 libraries
target_link_libraries(edge_detect
${rclcpp_LIBRARIES}
${geometry_msgs_LIBRARIES}
${turtlesim_LIBRARIES}
${std_srvs_LIBRARIES} # Link against std_srvs library
)
# Include directories
target_include_directories(edge_detect PUBLIC
$<BUILD_INTERFACE:${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/include>
$<INSTALL_INTERFACE:include>
${rclcpp_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${geometry_msgs_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${turtlesim_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${std_srvs_INCLUDE_DIRS} # Include std_srvs headers
)
# Suppress deprecated declaration warnings
add_compile_options(-Wno-deprecated-declarations)
# Install executable
install(TARGETS edge_detect
DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME})
# Add ament package
ament_package()
Building packages
Now with these files updated we can cd to our ~/ros_ws and build our fancy new package with colcon build like so:
colcon build --packages-select turtlesimAutomata
This will only build our new package, you can also run colcon build but specifying the package saves some time
Now we also need to source our setup.bash file with the following:
source install/setup.bash
Running the node
Finally we can test our code! Lets first open the turtlesim node with the following:
ros2 run turtlesim turtlesim_node
Now we can test our node with:
ros2 run turtlesimAutomata edge_detect
Look at our little turtle go :o

I also wrote this bash script to automate the install and running of this node, code below:
#!/bin/sh
# Make directory
mkdir ~/ros2_ws/src
# Copy Content
cp -r ~/Downloads/turtlesimAutomata/turtlesimAutomata ~/ros2_ws/src
# Remove folder and files
rm -r ~/Downloads/turtlesimAutomata
# Run turtle sim node
gnome-terminal -- bash -c "source ~/.bashrc;cd ~/ros2_ws;ros2 run turtlesim turtlesim_node"
# Run Edge detection node
gnome-terminal -- bash -c "cd ~/ros2_ws; sleep .5; colcon build --packages-select turtlesimAutomata; source install/setup.bash;ros2 run turtlesimAutomata edge_detect
"